
Compare and contrast positive and negative feedback. What are the components of the homeostasis model? What are the "fluid compartments" of the body? Describe the homeostasis of blood glucose and body temperature. Identify the organs that would be found in each abdominal quadrant 14. What are the ventral and dorsal body cavities of the body? What are the subcategories or each cavity? 13. Describe the different sections/planes of dissection such as coronal, transverse, sagittal planes? 12. Distinguish the anatomical terms: superior vs. Name the major organs associated with each system. Name the organ systems of the human body.

If there are any proteins (albumin for example), they pass to the lymphatic system. In contrast to what might be expected, the intestinal tight junctions are highly dynamic areas and their permeability can change in response to both external and intracellular stimuli. In the interstitial fluid, there are virtually no proteins. Although the plasma membrane is permeable to water. The ICF is separated from the Extracellular Fluid (see below) by the plasma membrane of each, individual cell.
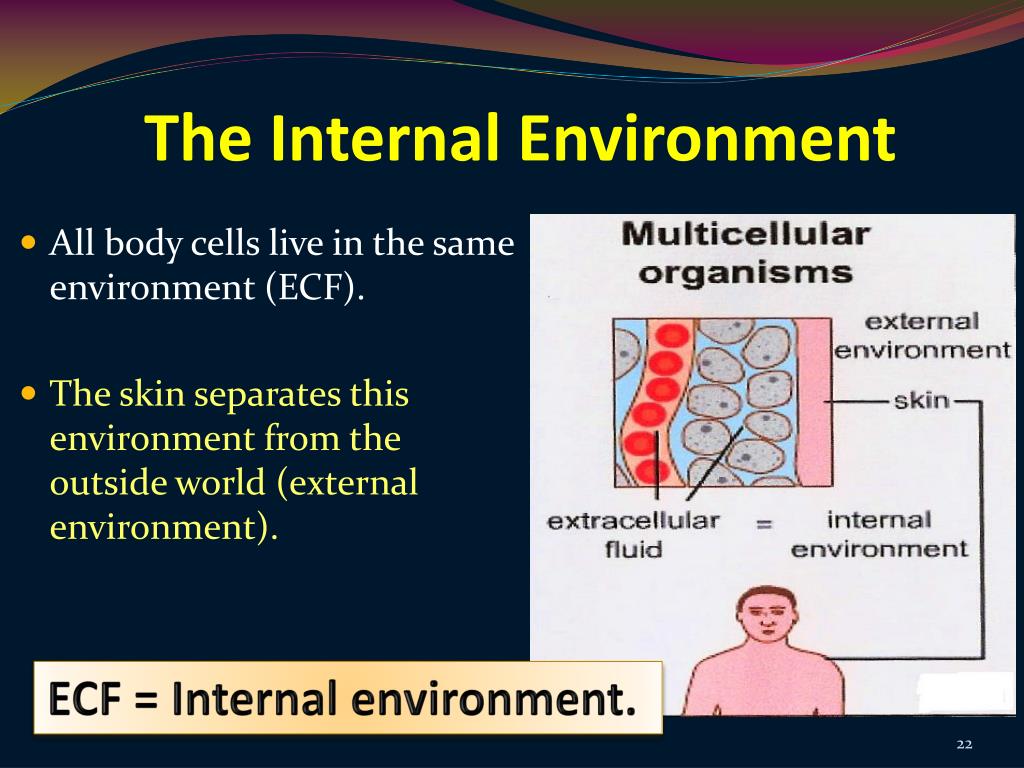
What is the hierarchical organization of life? Describe each level. They are involved in maintaining the cellular polarity and in the establishment of compositionally distinct fluid compartments in the body. The Intracellular Fluid (ICF) refers to the fluid present inside cells and is considered the sum total of the fluid volume in all of the body's cells. Compare and contrast anatomical & functional systems. What are the two general approaches in studying gross anatomy? What are examples of anatomi subdivisions? 3. What is the concept known as complimentarity? 2. Transcribed image text: Chapter 1: the Human Body: An Orientation 1.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
